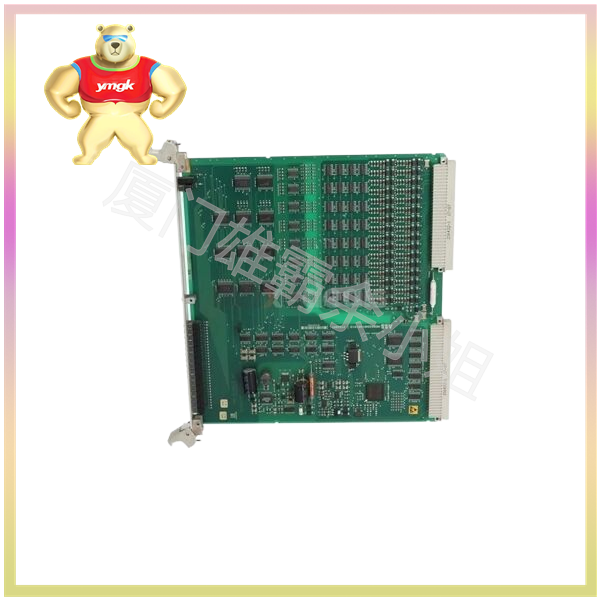
The output power circuit of PCB relay is just a component of the load current of the power switch; Everyone still defines PCB relays as communication AC or DC based on the data signal when the power switch is turned on. Due to the consideration of price, the power switches used for communication between AC and DC cannot be used separately on the same type of PCB relay, which may cause compatibility issues with magnetic induction. Similarly, due to heat dissipation and cost considerations, the construction of electronic components does not allow for multiple additional outputs, which can also pose challenges for magnetic induction compatibility.
DC output (DC PCB relay)
The output components of the DC output PCB relay can be selected as 2-wire or 3-wire output. The 2-wire output key is used to select PCB relays with control module packaging enclosures when the output current is below 10 amperes, while the 3-wire output is generally used for I/O control modules. In a 2-wire output power circuit, the load can be connected in series to any of the wiring terminals of the PCB relay, as long as the optical rotation of the power supply voltage meets the regulations.
When the output component is a dual transistor, the 2-wire interface method can avoid the transistor from completely saturating, which helps maintain the loss of 1.2-1.9VDC when the PCB relay is connected on both sides. This is acceptable in most application scenarios, especially when the load power supply voltage is high (>24VDC).
When the working standard voltage of the output terminal is low, such as in the data socket system software, a residual working voltage of 1.9VDC appears too high; In such situations, a 3-wire system can be used to achieve full saturation of the output transistor, resulting in a residual operating voltage of only 0.2-0.3VDC. I/O control modules are generally used between two low-voltage data system software or components as protective sockets, and therefore generally have 3-wire output PNP or NPN modes.
When the PCB relay is connected, the field-effect transistor is equivalent to a small resistor (50 to 80 milliwatts). According to Ohm’s Law, the output loss of PCB relays depends on the current size, for example, based on a current of 20A, the large current of PCB relays is about 1.2-1.9VDC.