- Controller and input/output module (I/O module).
(1) The controller is mainly composed of microprocessor chips and memory, namely the CPU module. In PLC control systems, the CPU module is equivalent to the human brain and heart. It continuously collects input signals, executes user programs, refreshes system outputs, and uses memory to store programs and data.
(2) I/O modules are input and output modules. The switch input and output modules are referred to as DI modules and DO modules, while the analog input and output modules are referred to as AI modules and AO modules. DI, DO, AI, and AO are collectively referred to as signal modules. The signal module is the eyes, ears, hands, and feet of the system, serving as a bridge connecting external field devices and CPU modules.
The digital input module is used to receive digital input signals from buttons, selection switches, digital dip switches, limit switches, proximity switches, photoelectric switches, pressure relays, etc. The analog input module is used to receive continuously changing analog current and voltage signals provided by potentiometers, speed generators, and various transmitters.
The switch output module is used to control output devices such as contactors, solenoid valves, electromagnets, indicator lights, digital display devices, alarm devices, etc. The analog output module is used to control actuators such as electric control valves and frequency converters.
- Sensors and actuators.
(1) A sensor is a detection device that can sense the information being measured and convert it into electrical signals or other required forms of information output according to certain rules to meet the requirements of information transmission and processing. It is used for storage, display, recording, and control. It is a part of achieving automatic detection and control.
(2) An actuator is a device that receives control information and applies control to the controlled object. The executing agency consists of two parts: the executing agency and the adjusting agency. The regulating mechanism directly changes the parameters of the production process through the executing mechanism, making the production process meet the predetermined requirements. The executing mechanism receives control information from the controller and converts it into the output of the driving and regulating mechanism (such as angular displacement or linear displacement output). According to the driving force used, the actuator is divided into three types: pneumatic, electric, and hydraulic.

- Human computer interaction.
The human-machine interface can be integrated with industrial control equipment such as programmable controllers, frequency converters, DC speed controllers, instruments, etc., using display screens to write working parameters or input operation commands through input units (such as touch screens, keyboards, mice, etc.) to achieve digital device human-machine interaction.
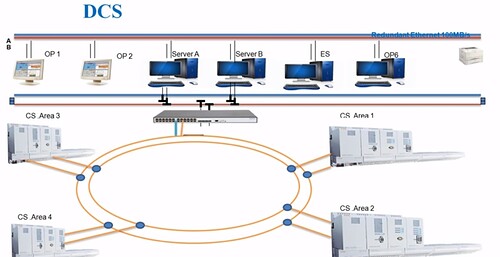
- Network communication.
Network communication processors can achieve communication between PLCs, remote I/O between PLCs, and connect PLCs to intelligent devices such as MPI, PROFIBUS-DP, AS-i, and industrial Ethernet, or be used for point-to-point communication.
- Programming device.
Programming equipment is an external device of PLC, which is a tool for programming and configuring programmable logic controllers, usually including handheld programmers and computers. There are two types of programmers: simple and intelligent. Simple programmers are generally used for small programmable controllers, while intelligent programmers are generally used for large and medium-sized programmable controllers. The function of a programmer is to compile user programs and send them to the PLC program memory. Use a programmer to check, modify, debug user programs and monitor PLC operating conditions online. Nowadays, many PLCs use computers as programmers and specialized software tools for programming or monitoring.
- Project management software.
Project management software can realize the visualization, diagnosis, and maintenance process control components of the entire system, provide an overview of the entire maintenance process, and complete the tracking and archiving of status changes and maintenance procedures. Currently, project management software typically includes programming software.