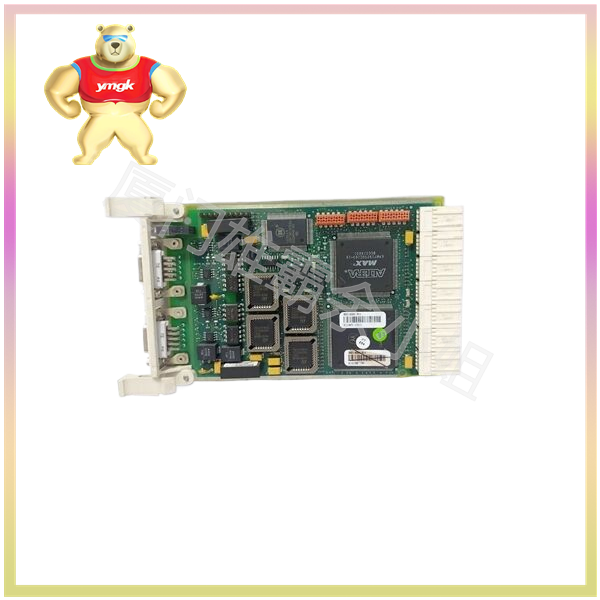
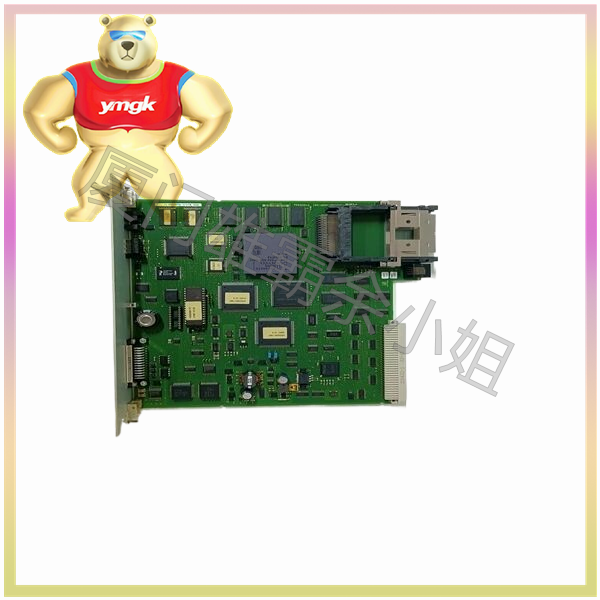
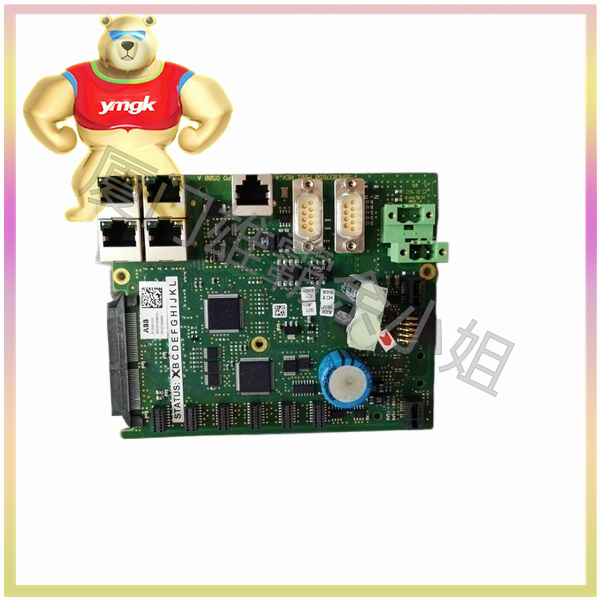
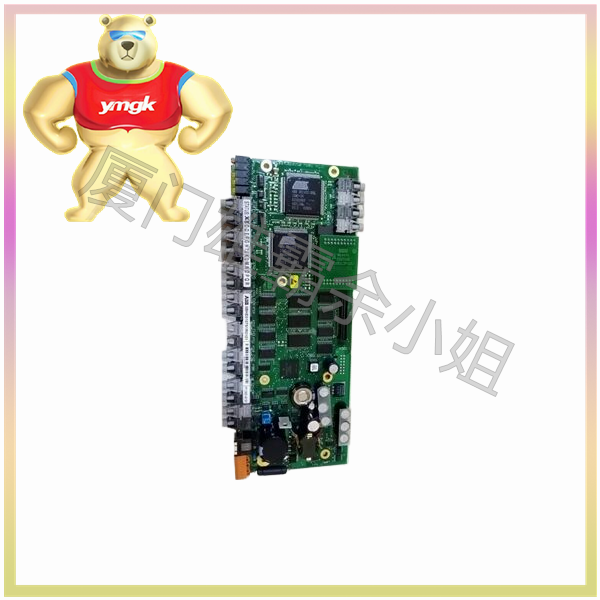
Advantages of power module:
- Simple design
At present, there are various types of modules on the market, including AC-DC, DC-DC, high voltage, etc. Simply choose a suitable power module and pair it with a small number of discrete components to use. The highly integrated circuit inside the module makes the design more compact, and suppliers can also provide professional technical support and system solutions. The biggest difference from the discrete type is that manufacturers can provide important data such as models, peripheral circuits, module parameter curves, etc.
- Save costs and time
The power module has multiple input and output options, and can be repeatedly or cross added to form a modular combination power supply, thereby achieving multiple input and output. Compared to standalone, debugging is simpler and safer, greatly simplifying design applications and shortening development time.
- High reliability
Modules generally use automated processes to ensure quality and reliability. The power module is selected by a professional power R&D team according to strict standards, designed and developed, and undergoes comprehensive reliability testing and mass production testing. However, it is more difficult to conduct in-depth testing for the split type scheme.
- High power, density, efficiency
Modules generally use multi-layer PCB aluminum substrates with high power density and small volume, saving system space. At present, the 1/4 bricks of DC-DC modules can reach up to 1000W, and the standalone scheme is difficult to meet such standards.
- Easy to maintain and flexible in design
In product applications, if a malfunction occurs, simply replace another module to ensure normal operation. If there is a need to change the plan during the design process, only the modules need to be modified, without modifying the overall power supply circuit.
- Widely used
It has been widely used in various fields such as instrumentation, automotive electronics, rail transportation, data communication, industrial automation, smart home, aerospace, military industry, scientific research experiments, ships, metallurgy and mining, power systems, medical electronics, security monitoring, new energy, petrochemicals, handheld electronic devices, etc.