Mark VIe Distributed Control System
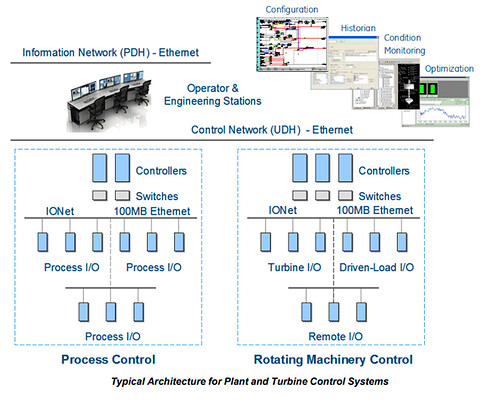
The Mark VIe distributed control system does not require a backplane and is based on Ethernet, which improves system availability and simplifies operation and maintenance throughout the entire lifecycle. Ethernet connection is essential to the foundation of industrial Internet.
The Mark VIe system replaces rack based control with flexible, high-speed, and low-cost communication at the lowest level of control system design.
I/O can be distributed or centralized, with primary and auxiliary control coexisting on the same network while maintaining functional independence. In addition, primary control can monitor safe inputs without interference, reducing the cost of replicating on-site instruments.
Overview of Mark Vie’s System
The core of the system is a single board controller. The controller includes a main CPU and redundant Ethernet drivers for I/O communication with the network, as well as additional Ethernet drivers for controlling the network. For the main processor and I/O modules, a real-time multitasking operating system is used. The control software is stored in non-volatile memory and written in a flexible control block language. It is similar to the IEEE 854 32-bit floating-point format and also provides Sequential Function Diagrams (SFC) for complex sequences.
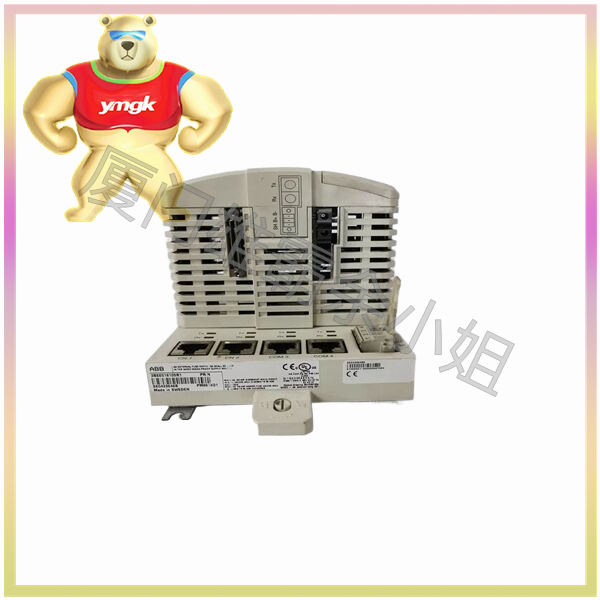
I/O network (IONet) is a point-to-point full duplex protocol. It provides a deterministic high-speed 100 MB communication network for local or decentralized I/O devices, as well as communication between the main controller and networked I/O modules. The online controller continuously reads input data from IONet and has single redundancy, dual redundancy, and triple redundancy configurations. Copper and fiber optic connections are both supported.
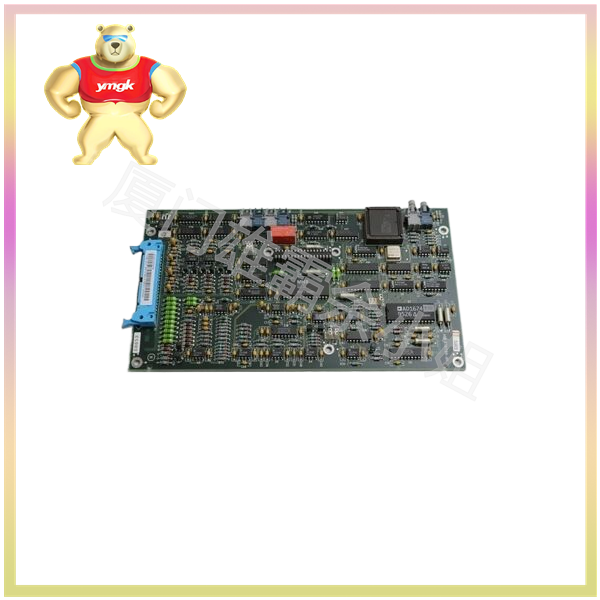
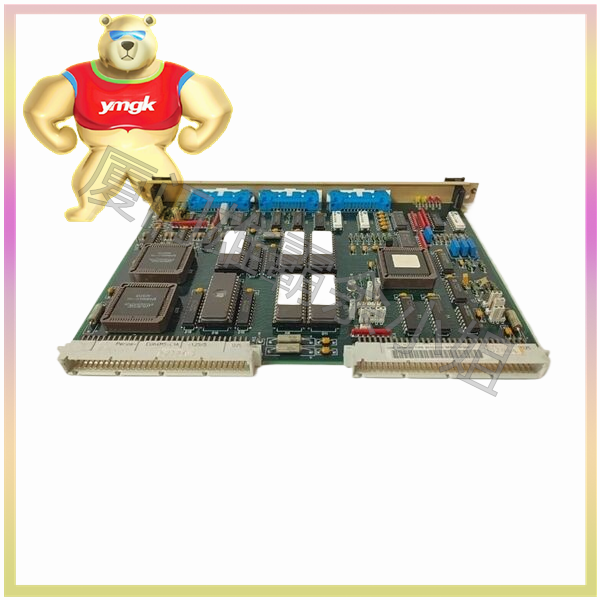
The Mark VIe I/O module consists of three basic components: terminal board, terminal board, and I/O components. The barrier or box type wiring board is placed on the terminal board, which is installed in the control cabinet on the d in guide rail or base. The I/O pack has two Ethernet ports, a power supply, a local processor, and a data acquisition board. With the addition of I/O packs to the control system, I/O capabilities are also enhanced, allowing for use in simplex, dual, or triple redundant configurations. Because some processing subsystems require higher throughput, the local processors in each I/O packet run algorithms at higher rates according to the needs of the application.
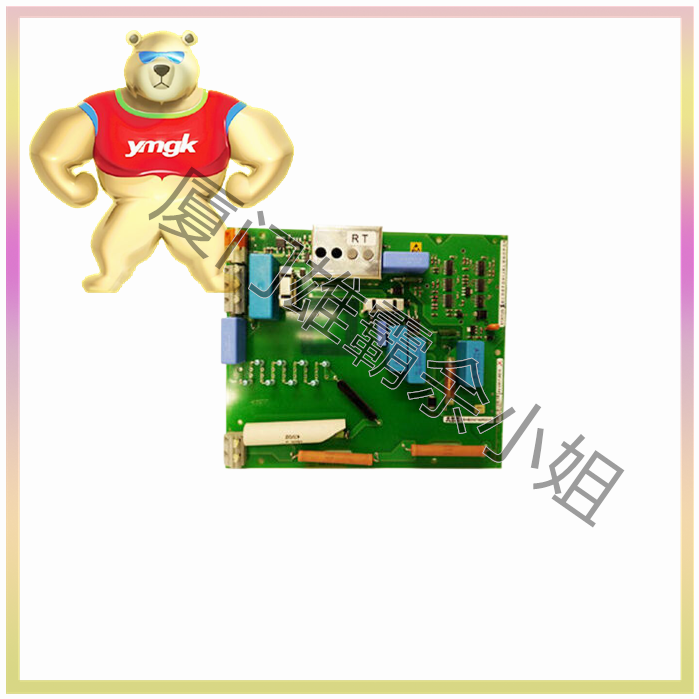
On output only modules and combination modules with discrete inputs and outputs, discrete outputs are accessible. Mechanical relays with dry “C” contacts are the most commonly used because they can be used in AC and DC circuits with different rated voltages, provide normally open and/or normally closed contacts, have no leakage current, and have the versatility required for melting, diagnosis, and solenoid suppression. There are several types of built-in solenoid interfaces that can save on the cost of external custom melting and suppression.