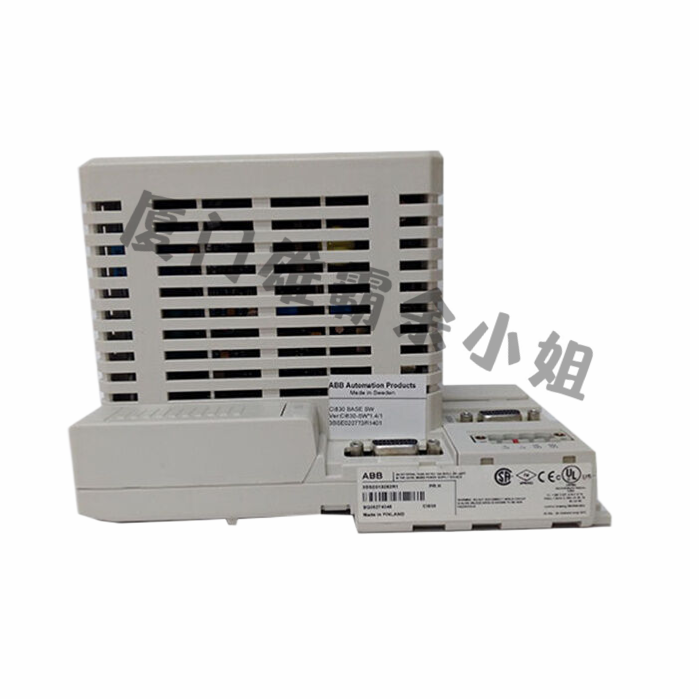
- The design of reliable DCS systems generally adopts redundancy design. Redundancy means designing key devices, CPUs, and various modules in a system in a sequential manner. If a processor or module fails, the backup device will immediately run. Alternatively, both actions can be taken simultaneously. This can reduce system failures caused by critical equipment failures.
- Open systems adopt a systematic, modular, and standardized open platform. All interconnected computer systems can achieve centralized interconnection and access through communication methods such as Ethernet. If it is necessary to add or reduce the system, system modules can be directly added or reduced, making the design and maintenance of the system easier.
With the development of modular DCS systems, there is a trend towards modular design. All core devices adopt modular design, including processors, power supplies, I/O modules, communication modules, and AI/AO modules. These devices are designed as independent modules. Regarding the assembly of the cabinet, only the base of the module needs to be installed, and the appropriate module can be installed on the base to install the hardware. Each module has its own CPU and processing capabilities, thereby improving processing speed. Meanwhile, each module does not interfere with each other. Even if one module has a problem, it will not affect other modules and supports hot swapping.
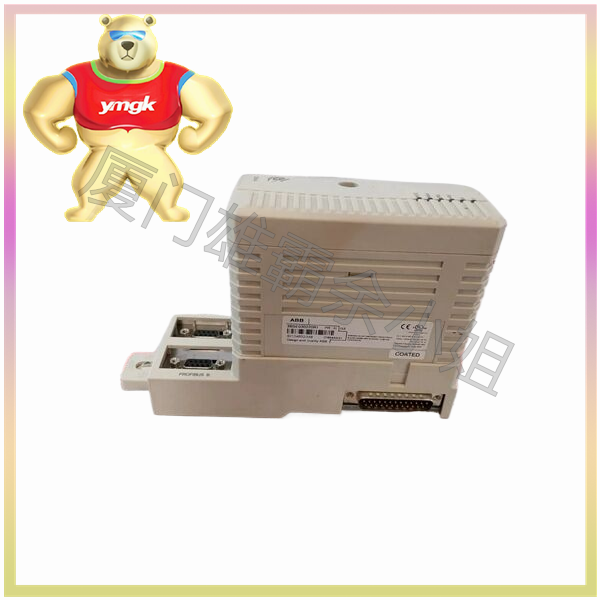

DCS, as a computer integrated system that integrates process control and monitoring, has become a complete system that combines computer, communication, display, and control. Driven by a continuous communication network. Its main characteristics are decentralized control, centralized operation, hierarchical management, flexible configuration, and convenient configuration. Nowadays, DCS can be widely used for production control and management of industrial equipment, and has been widely applied in process automation fields such as chemical, power, metallurgy, etc.