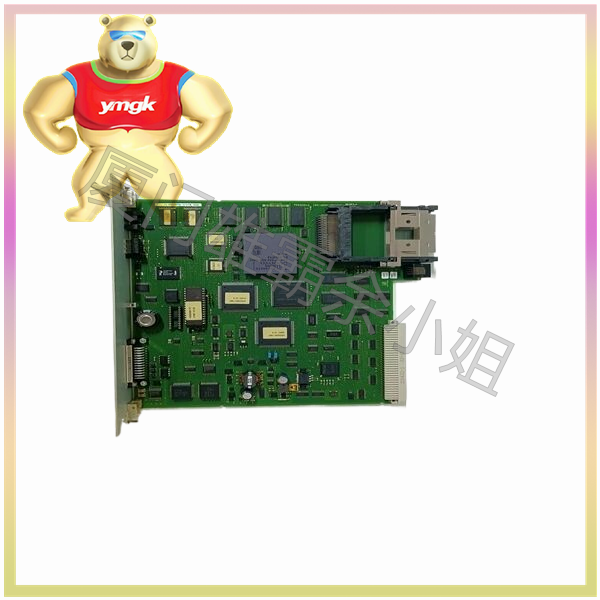
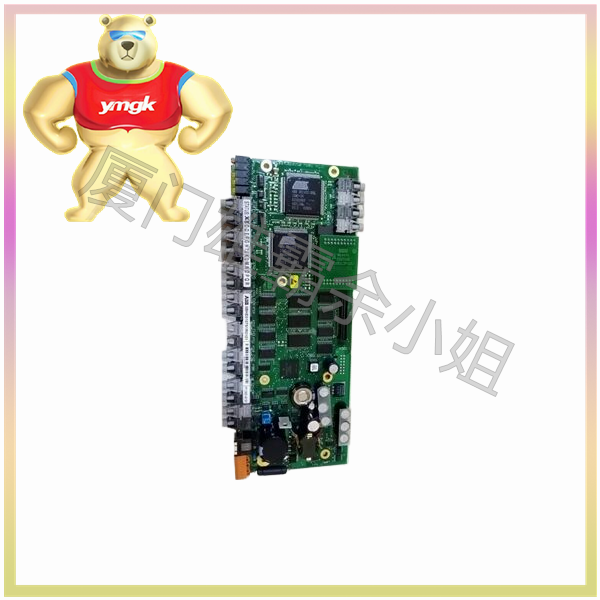
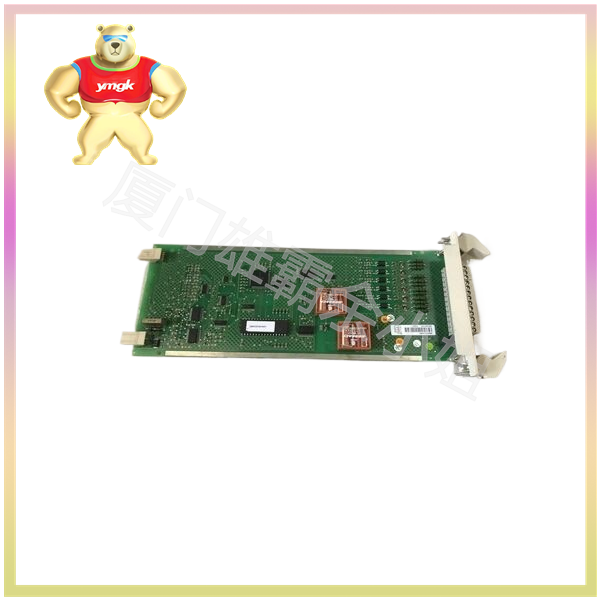
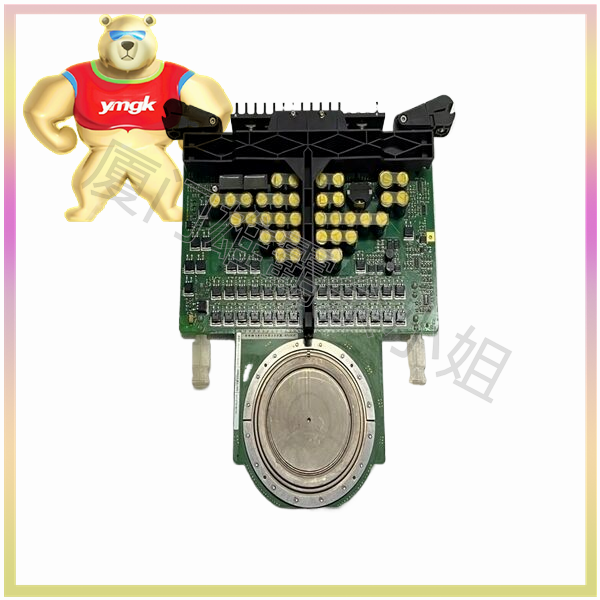
Composition and Function of Motor Controller
A motor controller is a device used to control and drive the operation of an electric motor, typically consisting of the following components:
- Power Supply: Provides the necessary electrical energy for the motor controller, usually DC or AC power.
- Control Unit: Responsible for receiving and processing signals from input devices such as switches and sensors, and generating corresponding control signals to control the operation of the motor.
- Circuit Protection: including overcurrent protection, overheating protection, voltage protection and other protection functions, used to ensure the safe operation of motors and controllers.
- Driver: Convert control signals into motor recognizable signals to control the speed, direction, and stop of the motor.
- Motor Interface: Provides interfaces for connecting motors, including motor power interface and motor signal interface.
- Feedback device: such as an encoder or sensor, used to detect the position, speed, and direction of rotation of a motor, and send feedback signals to the control unit to achieve closed-loop control.
- Communication Interface: Used for communication with other devices or systems, such as data exchange and command transmission with upper computers or other controllers.