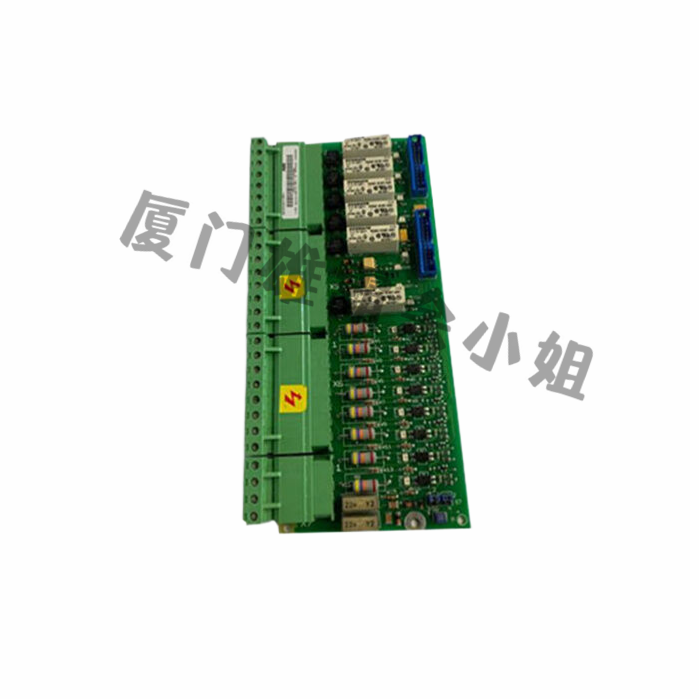
A relay is an electromagnetic switch that controls the switching state of contacts through the magnetic field generated by the current in the coil. Relay modules typically consist of an electromagnetic relay and a control circuit (such as switch circuits, sensor circuits, etc.).
Electromagnetic relay is the core part of relay module, which can convert the control signal of low-power circuit into the switching action of high-power circuit. Electromagnetic relays are generally composed of coils, moving iron cores, and contacts. When the coil is energized, it generates a magnetic field that magnetizes the moving iron core and attracts the contacts to close. When the coil is powered off, the magnetic field disappears, the moving iron core returns to its original state, and the contacts open.
The control circuit of a relay module is usually provided with control signals by a switch circuit or sensor circuit. For example, a button can be used to control the switching action of a relay. When the button is pressed, the control circuit will supply power to the coil of the relay, and the contacts will close; When the button is released, the coil loses power and the contacts open.