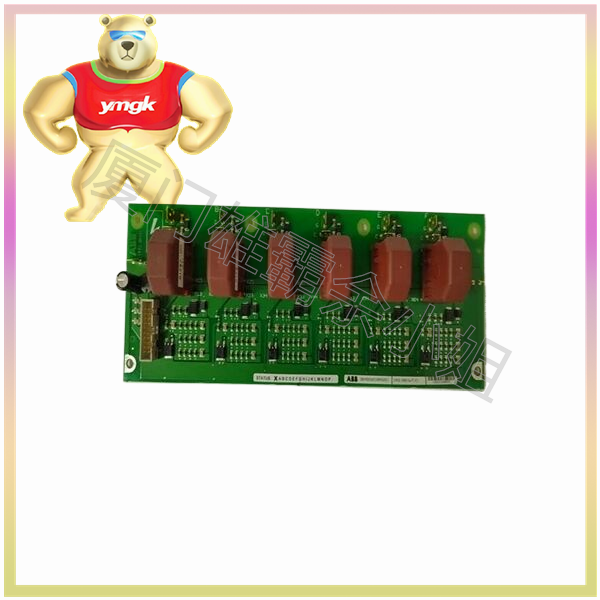
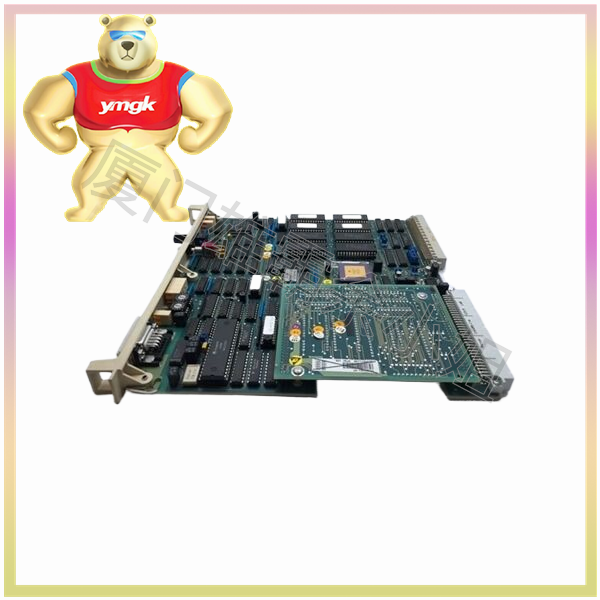
Servo controllers are usually composed of multiple modules, each with different functions, to achieve precise control of servo motors. Common servo controller modules include the following:
Controller motherboard: The controller motherboard is the core component of a servo controller, usually including a microprocessor, memory, signal receiving circuit, and output interface, used to receive control signals and control servo motors.
Power module: The power module is used to provide stable power to servo motors, usually including transformers, rectifiers, filters, etc.
Signal receiving module: The signal receiving module is used to receive control signals from the controller motherboard, usually including encoder interfaces, pulse input interfaces, etc.
Drive module: The drive module is used to control the motion and position of servo motors, usually including power amplifiers, drivers, pulse width modulators, etc.
Protection module: The protection module is used to protect servo motors and controllers, usually including overcurrent protection, overheating protection, overload protection, etc.
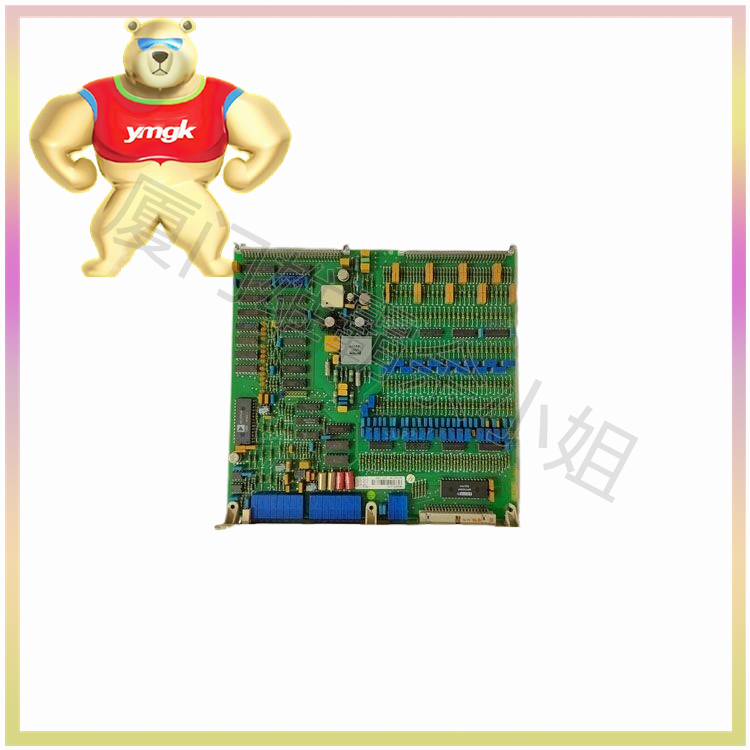
Communication module: The communication module is used for data exchange and control with other devices, usually including interfaces such as RS232, RS485, Ethernet, etc.
In short, the types and functions of modules in servo controllers vary depending on the manufacturer and specific model, and different module combinations may also differ according to different application scenarios.