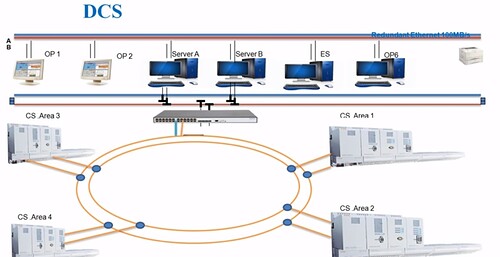
The working principle of the driver
A driver, also known as an actuator, is a device that converts electrical energy, pneumatic energy, hydraulic energy, and other energy into mechanical energy. Drivers are widely used in industrial automation, robotics, aerospace, automotive manufacturing, and other fields. This article will provide a detailed introduction to the working principle, classification, characteristics, and applications of drivers.

1、 The working principle of the driver
The working principle of the driver is to convert the input energy into mechanical energy through energy conversion, thereby achieving the driving of the load. The working principle of a driver can be divided into the following steps:
- Energy input: The driver receives input signals from the control system, such as electrical signals, gas signals, or liquid signals. These signals typically indicate the desired direction, speed, and force of motion.
- Energy conversion: The conversion mechanism inside the driver converts the input energy into mechanical energy. Common energy conversion methods include electromagnetic conversion, hydraulic conversion, and pneumatic conversion.
- Motion control: The motion control mechanism inside the driver controls the output direction, speed, and force of mechanical energy based on input signals to achieve precise driving of the load.
- Load driven: The driver transfers the converted mechanical energy to the load to generate the required motion.
- Feedback regulation: The driver collects motion information of the load through sensors, such as position, velocity, and acceleration, and feeds this information back to the control system. The control system adjusts the input signal based on feedback information to achieve precise control of the driver.
2、 Classification of Drivers
Drivers can be classified into the following categories based on their energy conversion methods:
- Electric drive: Electric drives convert electrical energy into mechanical energy through electromagnetic conversion. Electric drivers include DC motor drivers, AC motor drivers, stepper motor drivers, servo motor drivers, etc.
- Pneumatic actuator: Pneumatic actuators convert pneumatic energy into mechanical energy through pneumatic conversion. Pneumatic actuators include cylinders, pneumatic motors, and pneumatic fixtures.
- Hydraulic Drive: Hydraulic drives convert hydraulic energy into mechanical energy through hydraulic conversion. Hydraulic actuators include hydraulic cylinders, hydraulic motors, and hydraulic pumps.
3、 Characteristics of Drivers
- High efficiency: The energy conversion efficiency of the driver is high, which can convert most of the input energy into mechanical energy, thereby achieving efficient driving.
- High precision: The driver has high-precision motion control capability and can achieve precise driving of the load.
- High reliability: The design and manufacturing process of the driver are mature, with high reliability and stability.
- Easy to control: The interface between the driver and the control system is simple, making it easy to integrate with the control system.
- Strong adaptability: Drivers can choose different driving and control methods according to different application requirements.
4、 Application of Drivers
Drivers have a wide range of applications in industrial automation, robotics, aerospace, automotive manufacturing, and other fields. Here are some typical application scenarios:
- Industrial automation: Drivers are used in industrial automation production lines to achieve precise control of equipment such as robotic arms, conveyor belts, and lifting platforms.
- Robots: Drivers are used in the field of robotics to achieve precise driving of robot joints for complex motion control.
- Aerospace: Drivers are used in the aerospace field to achieve precise driving and control of aircraft, satellites, and other equipment.
- Automotive manufacturing: Drivers are used in the field of automotive manufacturing to achieve precise control of assembly robots, handling equipment, and other components on the production line.
5、 The development trend of drivers
With the continuous development of technology, the development trend of drivers is mainly reflected in the following aspects:
- High performance: The performance of the drive continues to improve, such as higher efficiency, higher accuracy, and higher reliability.
- Intelligence: The integration of drivers and control systems continues to improve, achieving more intelligent motion control.
- Greening: Drivers are increasingly focusing on energy conservation and environmental protection in their design and manufacturing processes, in order to reduce energy consumption and minimize environmental pollution.
- Miniaturization: With the development of microelectronics technology and micro machining technology, the volume of drivers is becoming smaller and smaller to meet the needs of micro devices.
- Customization: Based on different application requirements, the design and manufacturing of drivers are increasingly emphasizing customization to meet the needs of specific scenarios.
Summary:
Drivers, as devices that convert energy into mechanical energy, have a wide range of applications in industrial automation, robotics, aerospace, automotive manufacturing, and other fields. The working principle of a driver includes steps such as energy input, energy conversion, motion control, load driving, and feedback regulation. The main categories of drives include electric drives, pneumatic drives, and hydraulic drives. Drivers have the characteristics of high efficiency, high precision, high reliability, easy control, and strong adaptability. With the development of technology, the trend of driver development is manifested in high-performance, intelligent, green, miniaturized, and customized directions.