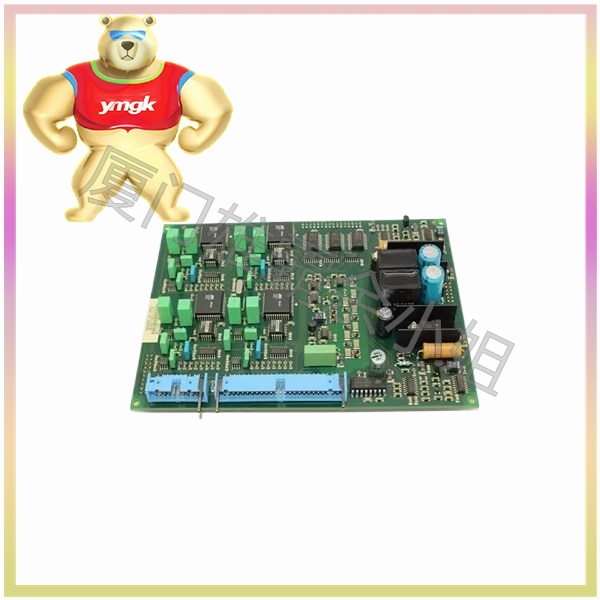
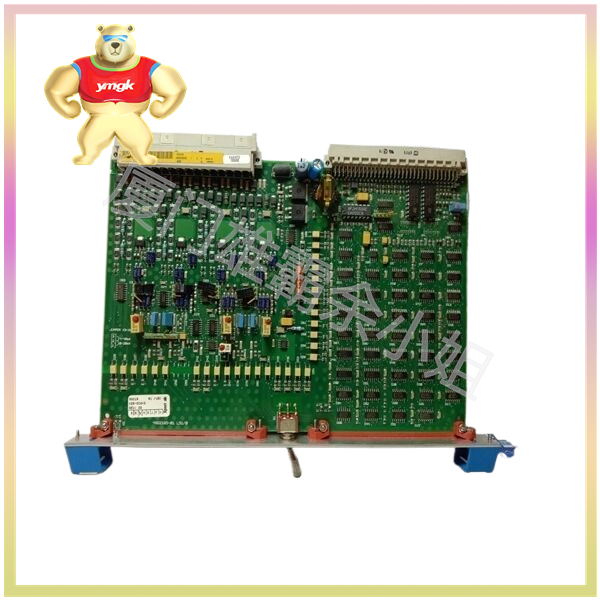
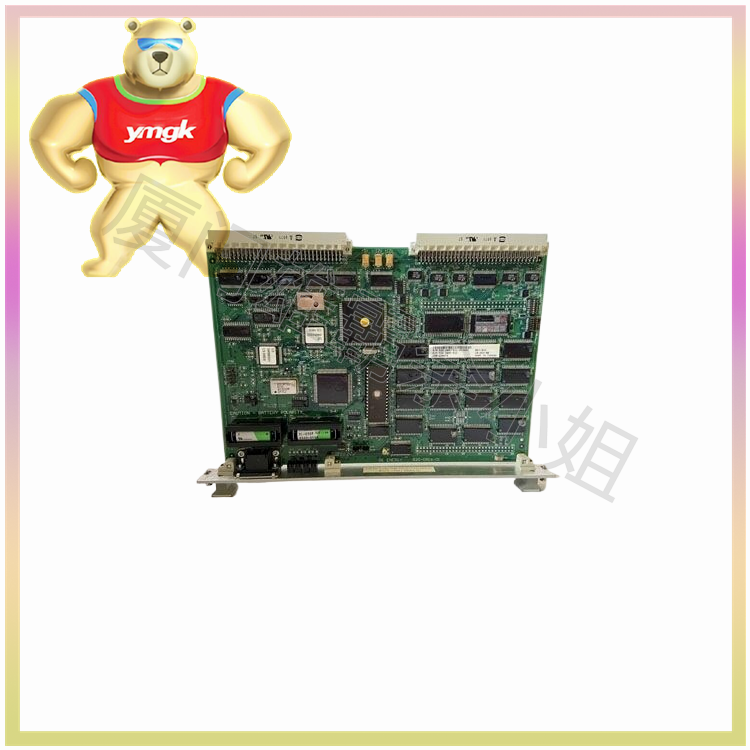
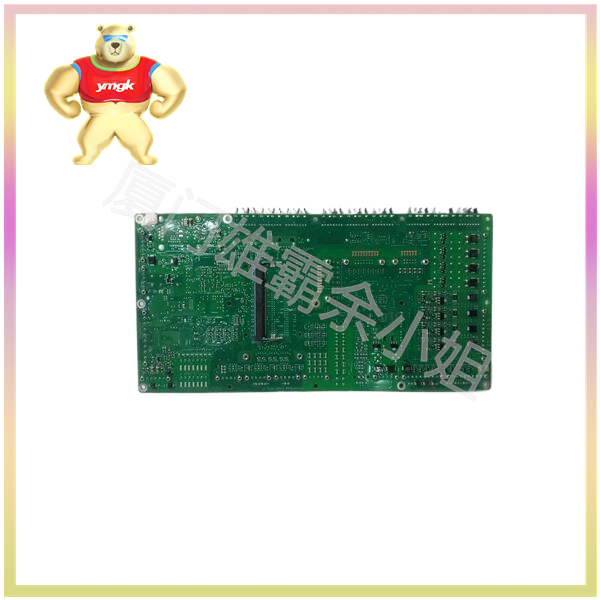
Different types of input-output circuits
Pilot work output
This type of output is typically used to drive high current electromagnetic loads such as solenoids, relays, valves, and motor starters. These loads have high inductance and exhibit significant surge currents.
The pilot load output should be able to withstand surge current of 10 times the rated load in a short period of time without failure.
Universal output
These are usually low voltage and low current, used to drive indicator lights and other non inductive loads. This type of module may or may not include noise suppression.
Discrete input
This type of circuit is used to detect the status of limit switches, buttons, and other discrete sensors. Noise suppression is crucial in preventing erroneous indications of input on or off caused by noise.
Similarly, output control is limited to devices that require simple switches, such as lamps, relays, solenoids, and motor starters.
Analog input/output
This type of circuit detects or drives analog signals.
Analog inputs come from devices such as thermocouples, strain gauges, or pressure sensors, which provide signal voltage or current from process variables. Standard analog input signal: 4-20mA; 0-10V.
By using sensors, analog outputs can be used to drive devices such as voltmeters, X-Y recorders, servo motor drivers, and valves. Standard analog output signal: 4-20mA; 0-5V; 0-10V.
The analog input interface module contains the circuits required to receive analog voltage or current signals from the on-site equipment of the liquid level transmitter. This input is converted from an analog value to a digital value for use by the processor.
Dedicated Input/Output
This type of circuit is used to interface PLCs with very special types of circuits, such as servo motors, stepper motor PID (proportional integral derivative) loops, high-speed pulse counting, rotary converters and decoder inputs, multiplexed displays, and keyboards.