What are PLC and DCS?
PLC definition: A digital operated electronic device that uses programming memory to store instructions internally to achieve specific functions such as logic, sequence, timing, counting, and arithmetic. It controls various types of machines or processes through digital or analog modules.
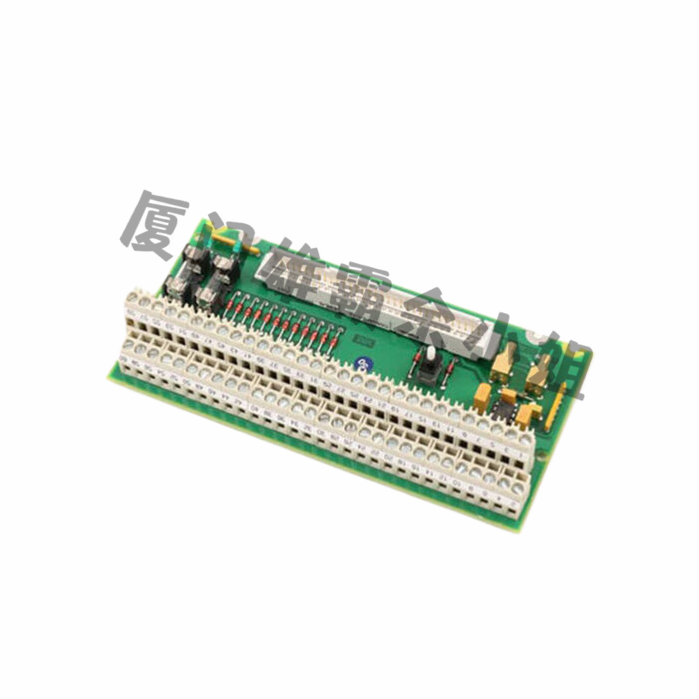

DC transmission system: DC transmission system 50 is a control system in production systems, processes, or any type of dynamic system, where element controllers are not centralized in one location but distributed to all systems, and each subsystem component is controlled by one or more controllers. The entire controller system is connected through a network for communication and monitoring.
The difference between PLC and DCS:
DCS is a control system that works in conjunction with multiple controllers, each designed to control a separate factory. Each controller can be a PLC
Basically, we can say that PLC is a machine control system, while DCS is used for process control.
PLCs are typically used for on/off (digital) control and can be extended with analog I/O modules to achieve analog control and be used for specific tasks. It controls the opening or closing of the only machine. DCS can control multiple PLCs simultaneously.
PLC can serve as a subsystem of DCS, with PLC dominating the control of high-speed machinery and DCS dominating complex continuous processes.
DCS has a wide communication range, while PLC does not have as many.
DCS is an automated distributed control system that can provide instructions for different parts of a machine. PLC is a digital computer used for automating electromechanical processes.
PLC must be offline to change any parameters. In DCS, it can be completed online.
Programming:
PLC programming is ladder logic, as DCS uses graphic function blocks that comply with SAMA standards.
In DCS, Boolean logic diagrams are easier to understand than separate analog logic diagrams and ladder logic diagrams. For PLC, using ladder logic to write analog PID control is a challenge.
PLC requires programmers to establish logical conditions and equations, and it does not have standard algorithms. In addition to having standard libraries for algorithms such as PID and lead lag,
Failure handling:
The diagnostic status of PLC is relatively limited and may only be indicative. It has limited use of diagnostic positions logically.
DCS can diagnose field level instruments, including HART and fieldbus devices. When a fault occurs, DCS I/O can select the HOLD-LAST or FAIL-SAFE position.
PLC does not support working in remote areas, DCS card has complete diagnostic and hot plug functions.