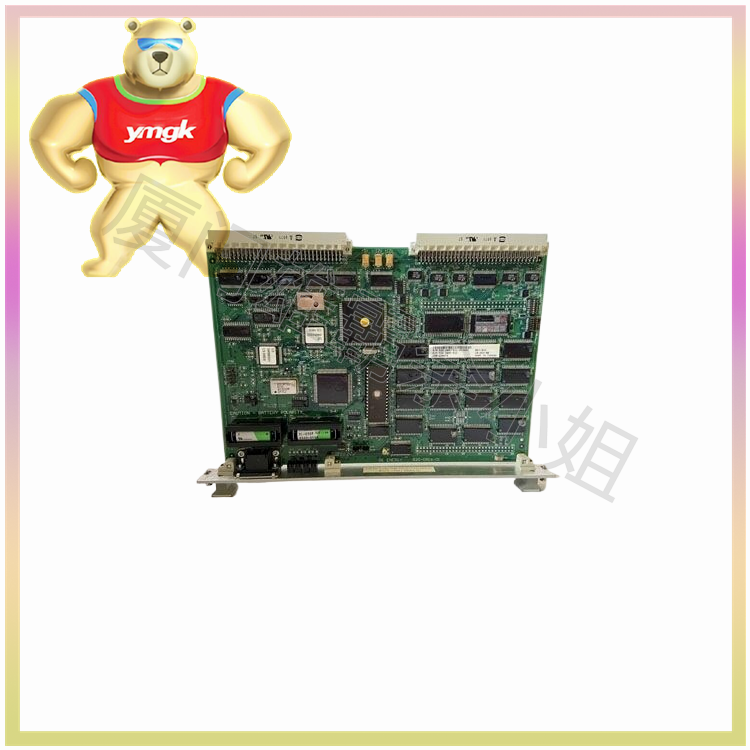
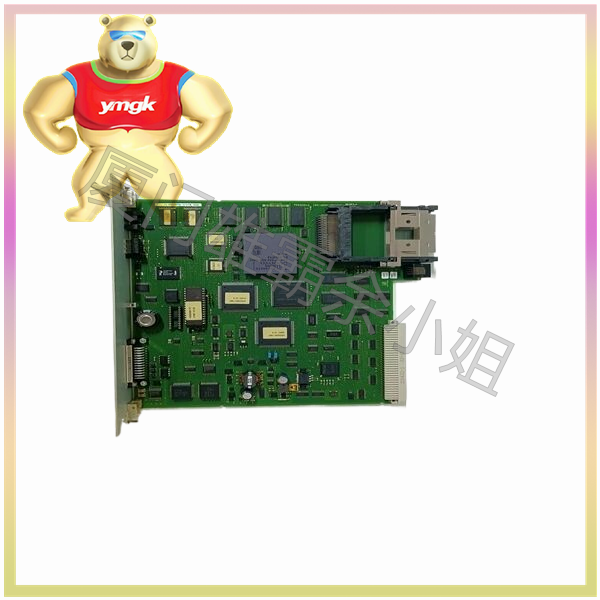
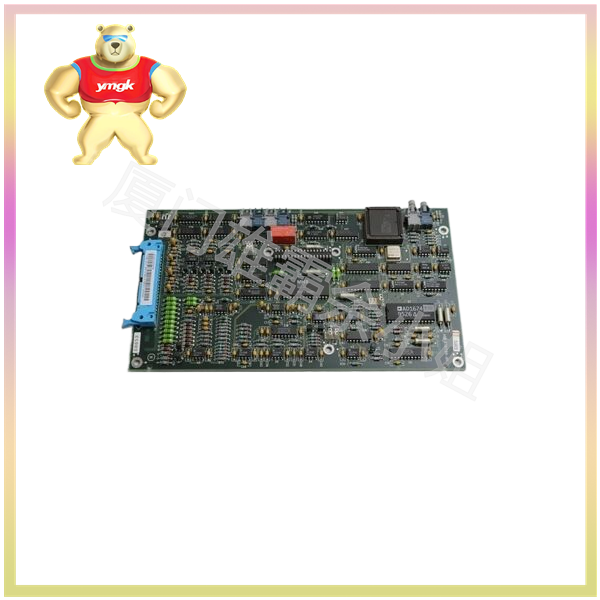
The function of servo drive
The servo motor controller is a key component in the field of numerical control systems and other related mechanical control. It controls the servo motor through position, speed, and torque to achieve high-precision positioning of the transmission system. Part of the servo system is mainly used in high-precision positioning systems.
The mainstream servo drives use digital signal processors as the control core, which can implement complex control algorithms, achieve digitization, networking, and intelligence. Power devices commonly use drive circuits designed with intelligent power modules as the core. IPM integrates drive circuits internally and also has fault detection and protection circuits for overvoltage, overcurrent, overheating, and undervoltage.
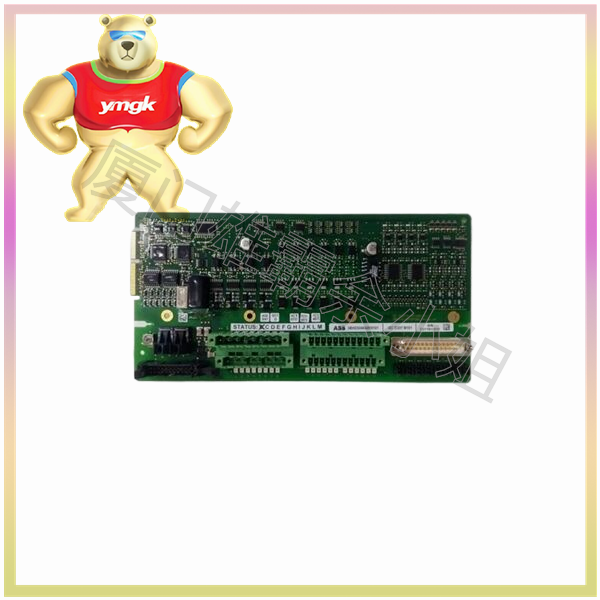
Servo drives are an important component of motion control and are widely used in automation equipment such as industrial robots and CNC machining centers. Especially for servo drives used to control AC permanent magnet synchronous motors, they have become a research hotspot both domestically and internationally. Vector based closed-loop control algorithms for current, velocity, and position are commonly used in servo drive design.
Difference between servo drive and frequency converter
The definitions of servo drive and frequency converter are different
A driver, also known as a servo controller or servo amplifier, is a controller used to control servo motors. Its function is similar to that of a frequency converter acting on a regular AC motor. It belongs to the servo system and is mainly used for high-precision positioning systems.
A frequency converter is a power control device that utilizes the switching function of power semiconductor devices to convert a power frequency source into another frequency. It has achieved functions such as soft starting, variable frequency speed regulation, improving operating accuracy, and changing power factor of AC asynchronous motors.
The overload capacity of servo drives and frequency converters is different
In general, the driver has a 3-fold overload capacity, which can be used to overcome the inertia moment of the inertial load during startup, while the frequency converter generally allows for a 1.5-fold overload.
Servo drives and frequency converters have different control accuracies
The control accuracy of the driver is much higher than that of the frequency converter. The control accuracy of the drive motor is usually ensured by the rotary encoder at the rear end of the motor shaft, and some transmission systems even have a control accuracy of up to 1:1000.
Servo drives and frequency converters have different applications
Inverter and driver are two types of control, the former belongs to the field of transmission control and the latter belongs to the field of motion control. One is to meet the requirements of general industrial applications and pursue low cost with low performance requirements for application scenarios. The other is to pursue high precision, high performance, and high response.