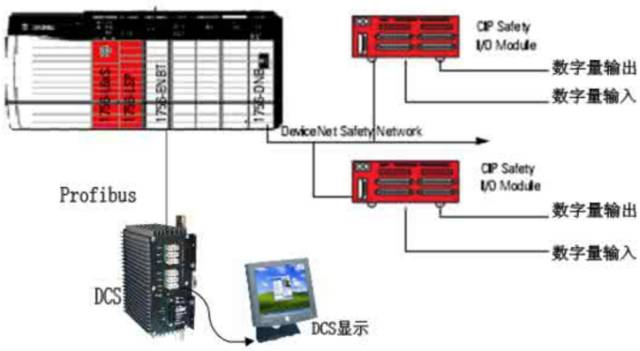
The configuration methods of PLC redundant systems mainly include the following:
Dual machine hot backup configuration
Dual machine hot backup configuration is the most common configuration method in PLC redundant systems. In this configuration, two identical PLC controllers are used, one as the main controller and the other as the backup controller. The main controller is responsible for real-time control of the system’s operation, while the backup controller monitors the main controller’s operational status in real-time. When the main controller fails, the backup controller can immediately take over the control task to ensure the continuous operation of the system.
Advantages: Fast switching speed, which can minimize the impact of system failures on the production process.
Disadvantages: Additional hardware and software resources are required, resulting in higher costs.
Dual machine cold backup configuration
Unlike the dual machine hot backup configuration, the backup controller in the dual machine cold backup configuration does not participate in real-time control tasks, but is in standby mode. When the main controller fails, it is necessary to manually switch the backup controller to the working state.
Advantages: Relatively low cost, as the backup controller does not require real-time operation.
Disadvantages: Slow switching speed, may require some downtime.
Multi machine backup configuration
In more complex application scenarios, it may be necessary to use multiple PLC controllers for redundant configuration. This configuration method can further improve the reliability and stability of the system. Multi machine backup configuration can be flexibly designed according to specific needs, such as three machine hot backup, four machine cold backup, etc.
Advantages: Able to handle more complex fault situations, improve system reliability and stability.
Disadvantages: High cost, requiring more hardware and software resources.
4、 The working principle of PLC redundant system
The working principle of PLC redundant system is mainly based on the following aspects:
Data synchronization
In a PLC redundant system, real-time data synchronization is required between the main controller and the backup controller. This includes control programs, input/output states, intermediate variables, etc. Through data synchronization, the backup controller can real-time understand the operating status of the main controller, so as to take over control tasks when needed.
Fault detection
The PLC redundant system needs to be able to detect the fault status of the main controller in real time. This is usually achieved through a combination of hardware and software. For example, hardware watchdog circuits can be used to detect the operating status of PLC controllers; At the same time, software can also determine whether there is a fault by detecting the execution status, input/output status, etc. of the control program.
Automatic switching
When a fault is detected in the main controller, the PLC redundant system needs to be able to automatically switch to the backup controller. This is usually achieved through pre-set switching logic. The switching logic can be flexibly designed according to specific needs, such as time-based switching, fault type based switching, etc.
Redundancy management
In order to ensure the stable operation and maintainability of the system, PLC redundant systems also need to undergo redundancy management. This includes the configuration of redundant resources, fault handling, system recovery, and other aspects. Through redundancy management, it can be ensured that the system can quickly restore its normal operating state in the event of a failure.