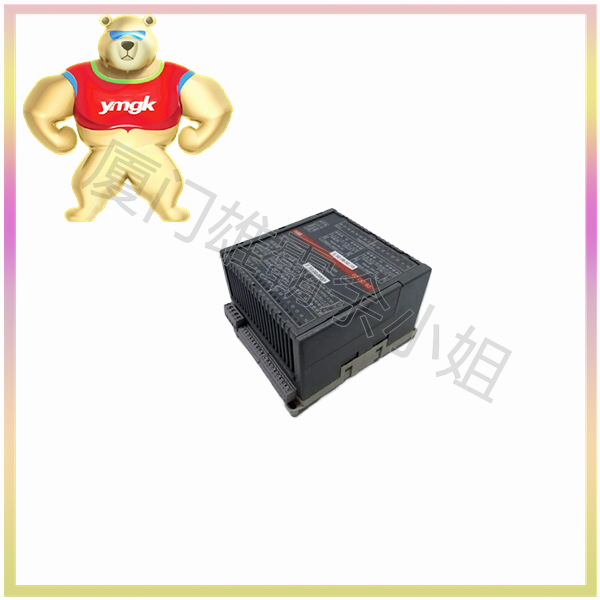
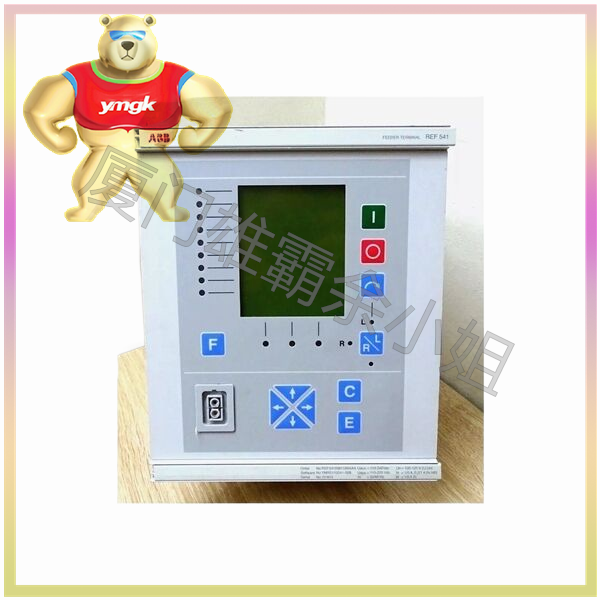
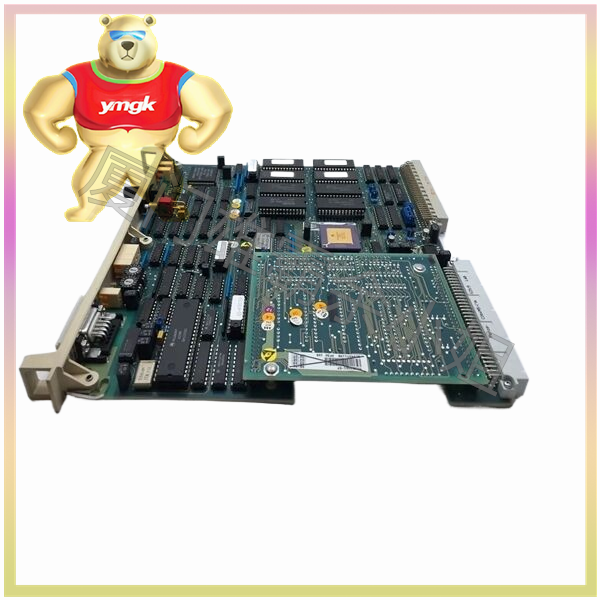
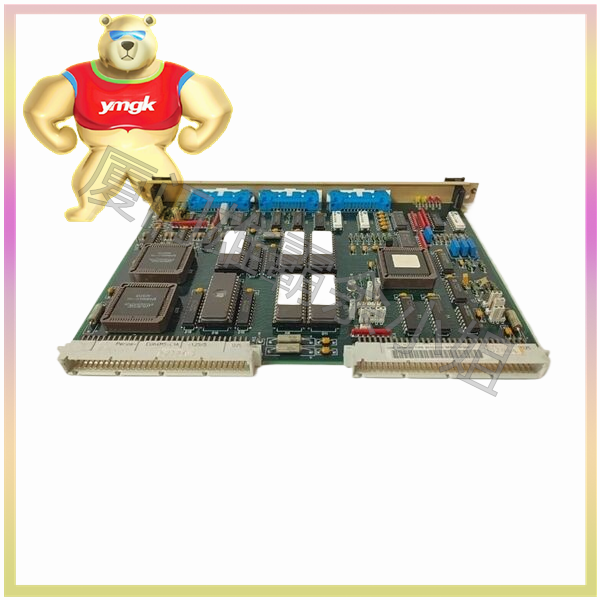
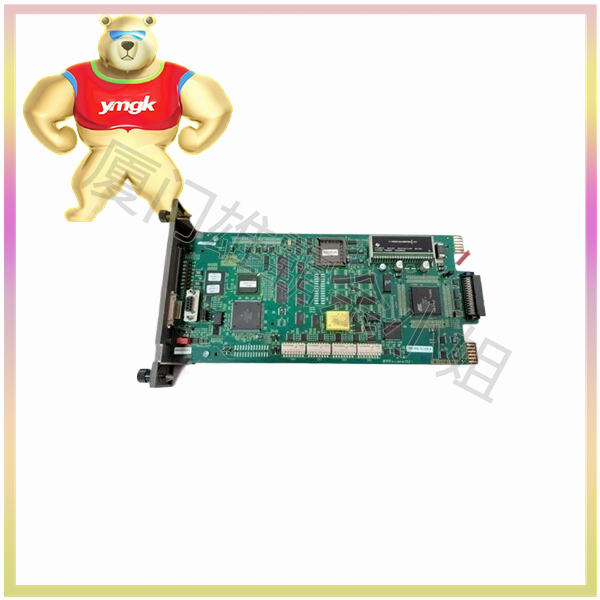
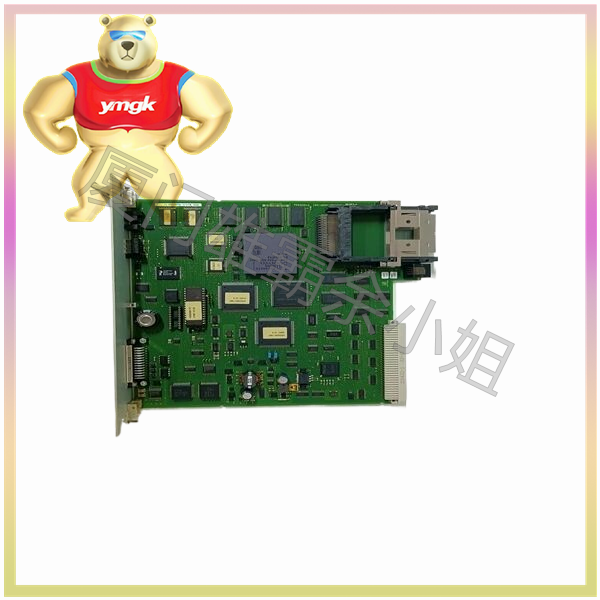
The motor controller mainly consists of the following parts:
Input interface: The input interface is responsible for receiving external control signals, such as switch signals, analog signals, etc. The input interface can be digital input, analog input, or pulse input, etc.
Control unit: The control unit is the core part of the motor controller, responsible for processing input signals and generating control instructions. Control units typically use microprocessors, digital signal processors (DSPs), or programmable logic controllers (PLCs).
Drive circuit: The drive circuit is responsible for converting the control instructions output by the control unit into voltage and current signals suitable for motor drive. The driving circuit usually includes power amplifiers, switching devices, etc.
Protection circuit: The protection circuit is used to protect the motor and controller from abnormal conditions such as overload, overheating, and overvoltage. Protection circuits usually include overload protection, overheating protection, overvoltage protection, etc.
Communication interface: The communication interface is used to exchange data between the motor controller and other devices. The communication interface can be serial communication, Ethernet communication, CAN bus communication, etc.
Display and operation interface: The display and operation interface is used to display the working status and parameters of the motor controller, as well as provide an interface for user operation. The display and operation interface can be LCD display screen, touch screen, buttons, etc.